In this article, we connect a KY-003 Hall Magnetic Sensor to a Raspberry Pi Pico 2, any rp2350 type board will be suitable. There are many good ones, I actually used a Pimoroni one as it was on hand
Overview
We will use Micropython for these examples but of course you can use the Arduino IDE as well if you have Raspberry Pi Pico support enabled
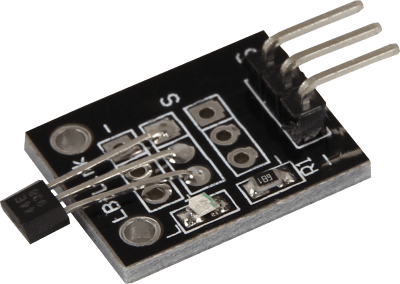
This module uses a 3144EUA-S Hall-effect switch IC
A Hall effect sensor is a device that detects the presence, strength, and direction of a magnetic field. Named after physicist Edwin Hall, who discovered the phenomenon in 1879, the Hall effect occurs when a current-carrying conductor or semiconductor is exposed to a perpendicular magnetic field.
This interaction produces a voltage, called the Hall voltage, across the material. Hall effect sensors leverage this principle to measure magnetic fields and convert them into electrical signals for a variety of applications.
These sensors are widely used in both industrial and consumer applications due to their versatility and reliability. In the automotive industry, they are employed for detecting the position of crankshafts, camshafts, and throttle levels, as well as for anti-lock braking systems (ABS). In consumer electronics, Hall effect sensors enable features like detecting open and closed positions in laptops and smartphone covers.
Additionally, they are used in robotics, brushless DC motors, and proximity sensing. Hall effect sensors come in digital or analog forms, with some providing a simple on/off signal when a magnetic threshold is met, while others offer precise measurements of magnetic field strength for more advanced applications.
The sensor looks like this
Parts Required
You can connect to the module using dupont style jumper wire.
| Name | Link |
| Raspberry Pi Pico 2 | |
| 37 in one sensor kit | |
| Connecting cables |
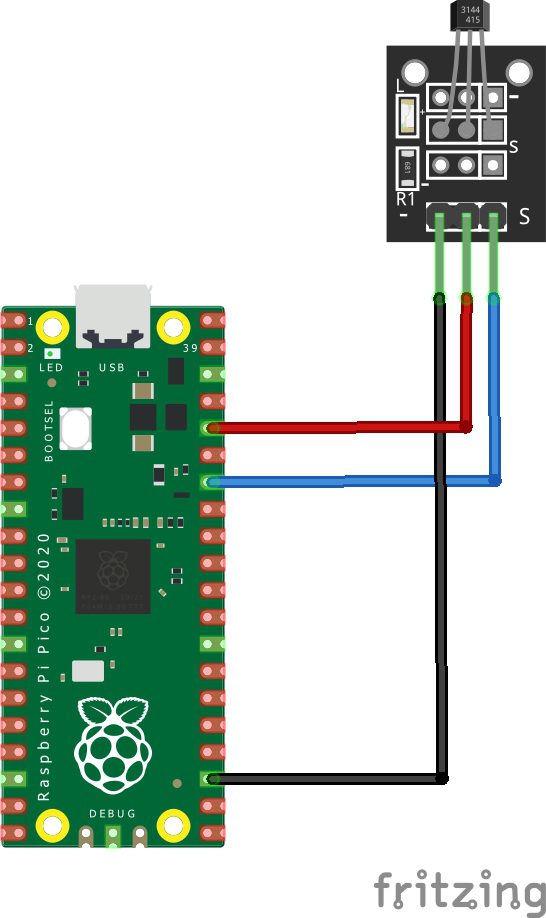
Schematic/Connection
| Pico | SENSOR |
|---|---|
| GPIO28 | S |
| 3v3 | + |
| GND | – |
The part I had was Pico but the pinout for a Pico 2 is the same – so this works fine
Code Examples
Basic example
from machine import Pin, Timer
from time import sleep
# Initialization of GPIO28 as input
sensor = Pin(28, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
# Continuous loop for continuous serial output
while True:
if sensor.value() == 0:
print("No magnetic field")
else:
print("Magnetic field")
print("---------------------------------------")
sleep(0.5)
REPL Output
You will need to find a magnetic source and move it close to the sensor, you can see the results here
>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
No magnetic field
—————————————
No magnetic field
—————————————
No magnetic field
—————————————
No magnetic field
—————————————
No magnetic field
—————————————
Magnetic field
—————————————
Magnetic field
—————————————
Magnetic field
—————————————
